Uncategorized Sunday, 2024/02/18
Many epithelial organs undergo branching morphogenesis during development, resulting in the construction of complex dendritic networks and the acquisition of specialized tissue structures. Understanding the establishment and maintenance of organizational structure is a core issue in developmental biology, which directly impacts organ physiology and diseases. In adult life, the loss of organizational structure may occur in the early stages and various human cancers. However how these processes are coordinated and how to preserve tissue structure in the event of severe cell rearrangement during organ development is still unclear.
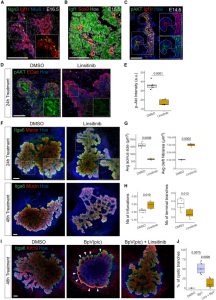
Recently, Professor Jean Francois Darrigrand and his team from the Centre for Gene Therapy and Regenerative Medicine at King's College London, UK, have discovered that pancreatic ductal cells undergo apical division by protruding and pulling the apical basement membrane to form cracks, using in vitro and in vivo mouse models. The insulin growth factor (IGF)/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway finely regulates the fluidity of pancreatic ductal tissue by controlling this process, while also affecting the acquisition of branching and cell fate. Through this study, the aim is to explain how the proliferation of pointed structures and branching occurs synchronously during the development of pancreatic organs.
Our Featured Products
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Source | Species | Tag |
| IGF1-06H | Recombinant Human IGF1 protein | E.coli | Human | N/A |
| IGF-08H | Recombinant Human Long Arg3 Insulin-like Growth Factor-I | E.coli | Human | N/A |
| IGF1-057H | Active Recombinant Human IGF1 Protein | E. coli | Human | |
| IGF1-09H | Active Recombinant Human IGF1 protein | Rice Grain | Human | N/A |
| PIK3CA-1894H | Active Recombinant Human PI3 kinase (p110α/p85α) protein, GST-tagged | Insect Cell | Human | GST |
| PIK3CA&PIK3R3-152H | Active Recombinant Human PIK3CA/PIK3R3 protein, His-tagged | Insect Cell | Human | His |
| PIK3CA-70H | Recombinant Human PIK3CA protein, Flag-tagged, Biotinylated | Insect Cell | Human | Flag |
| PIK3CA-2690HF | Active Recombinant Full Length Human PIK3CA Protein, DDK-tagged, Biotinylated | Insect Cell | Human | DDK |
| JAG1-3138H | Active Recombinant Human JAG1, Fc tagged | HEK293 | Human | Fc |
| JAG1-3226H | Active Recombinant Human JAG1 protein, His-tagged | HEK293 | Human | His |
In summary, this study opens up prospects for fine-tuning the IGF/PI3K signal, which may help reconstruct niches in the body and provide a starting point for promoting the branching of human pancreatic organ tissues.
Related Products and Services
Immune Checkpoint Proteins Protein Interaction Service Protein Expression and Purification Services Biomarker Service Drug Discovery Screening Protein Pathway Profiling Protein Expression Microarray
Reference Darrigrand JF, Salowka A, et. Acinar-ductal cell rearrangement drives branching morphogenesis of the murine pancreas in an IGF/PI3K-dependent manner. Dev Cell. 2024 Jan 13:S1534-5807(23)00691-3. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2023.12.011. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 38237591.
