Uncategorized Tuesday, 2024/06/11
Zhu Di and Wang Mingwei from Fudan University jointly published a research paper titled "Targeting BCL9/BCL9L enhances antigen presentation by promoting conventional type 1 dendritic cell (cDC1) activation and tumor infiltration" in Signal Transmission and Targeted Therapy. This study indicates that targeting BCL9/BCL9L enhances antigen presentation by stimulating cDC1 activation and infiltration into tumors. Knockout mice with novel inhibitors hsBCL9z96 or BCL9/BCL9L can significantly delay tumor growth and promote anti-tumor CD8+T cell response by inhibiting BCL9/BCL9L.
Mechanistically, targeting BCL9/BCL9L promotes antigen presentation in tumors. This is due to the increased activation of cDC1 and tumor infiltration along the XCL1-XCR1 axis. Importantly, using single-cell transcriptomic analysis, it was found that cDC1 deficient in Bcl9/Bcl9l is superior to wild-type (WT) cDC1 in activation and antigen presentation through NF - κ B/IRF1 signaling. Studies have jointly demonstrated that targeting BCL9/BCL9L plays a crucial role in the cDC1 regulation of tumor-derived antigen presentation, CD8+T cell activation, and tumor infiltration. Targeting BCL9/BCL9L to regulate cDC1 function and directly coordinating the positive feedback loop required for optimal anti-tumor immunity can serve as a potential strategy for combating immunosuppression and enhancing cancer immunotherapy.
Our Featured Products
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Species | Source | Tag |
| BCL9-10190H | Recombinant Human BCL9, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| BCL9-1243H | Recombinant Human BCL9 protein, His & T7-tagged | Human | E.coli | His/T7 |
| BCL9-2356M | Recombinant Mouse BCL9 Protein | Mouse | Mammalian Cell | His |
| Bcl9-1244M | Recombinant Mouse Bcl9 protein, His & T7-tagged | Mouse | E.coli | |
| BCL9L-169H | Recombinant Human BCL9L Protein, GST-tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| BCL9L-2357M | Recombinant Mouse BCL9L Protein | Mouse | Mammalian Cell | His |
| BCL9L-1002M | Recombinant Mouse BCL9L Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| XCL1-160H | Active Recombinant Human XCL1, MIgG2a Fc-tagged | Human | CHO | Fc |
| XCL1-28843TH | Recombinant Human XCL1, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| XCR1-0182H | Active Recombinant Human XCR1 Full Length Transmembrane protein(Nanodisc) | Human | HEK293 | N/A |
| BATF3-5069H | Recombinant Human BATF3, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| BATF3-425H | Recombinant Human BATF3 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
Antigen presentation is essential for anti-tumor response. In order to induce effective anti-tumor CD8+T cell responses, antigen presentation must be successful in two main events: first, tumor antigens are captured by antigen-presenting cells (APCs), processed into peptide fragments, and presented on APCs with major histocompatibility complexes class I (MHC-I) or human leukocyte antigen class I (HLA-I) to trigger CD8+T cells. Secondly, activated CD8+T cells recognize tumor antigens directly presented by APC and then kill tumor cells.
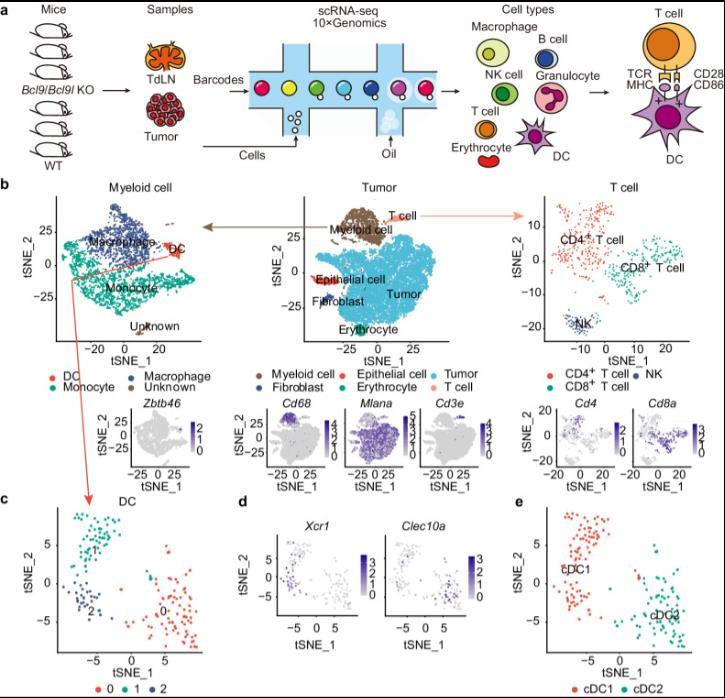
The traditional type 1 dendritic cells (cDC1) are considered to be the dominant subset of DCs that present tumor antigens to MHC-I to trigger CD8+T cells. Previous studies have shown that mice with BATF3 −/− selective deficiency of cDC1 exhibit cross-presentation defects and impair anti-tumor immunity. In human cancer, increasing evidence suggests that intratumoral cDC1 is associated with improved prognosis and response to cancer immunotherapy. However, DCs often have dysfunctions, immaturity, and even immunosuppressive effects within the tumor microenvironment (TME), lacking antigen presentation ability for cross primers. In addition, cDC1 is rare because TME excludes cDC1 from tumors through various mechanisms. Therefore, methods aimed at enhancing antigen presentation may promote anti-tumor immunity and improve cancer immunotherapy.
The Wnt/β - catenin signaling pathway is not only crucial in regulating tumor carcinogenesis, but also beneficial for immune invasion in many malignant tumors. An increasing number of studies have reported that the Wnt/β - catenin signaling pathway regulates DC function. The loss of β - catenin in CD11c+DC during startup weakened the tumor-induced inhibition of memory CD8+T cell response. The absence of LDL receptor-associated protein 5/6 (LRP5/6) in CD11c+DCs can inhibit tumor growth and increase anti-tumor response. The down-regulation of β - catenin or constitutive active glycogen synthase kinase 3 β (GSK3 β) in DC also enhances its function. In addition, Wnt1 promotes transcriptional silencing of CC/CXC chemokines in cDCs, inducing immune resistance in lung adenocarcinoma. In addition, the active Wnt/β - catenin signaling pathway inhibits the recruitment of CD103+DCs by CCL4 and CCL5 towards tumors.
B-cell lymphoma 9 and B-cell lymphoma 9 like (BCL9/BCL9L) serve as transcription co-activators of β - catenin and are crucial in the Wnt/β - catenin signaling pathway. The expression of BCL9/BCL9L is elevated in various human cancers and is associated with poor prognosis in cancer patients. Previous studies have reported that inhibiting BCL9/BCL9L promotes anti-tumor response through multiple mechanisms. CDC1 has been recognized to play an important role in the cross-presentation of CD8+T cell initiation and cancer immunotherapy. However, it is still unclear whether targeting BCL9/BCL9L controls antigen presentation, especially in the antigen presentation of cDC1 in anti-tumor immunity.
This study reported that inhibition or depletion of BCL9/BCL9L significantly inhibited tumor growth and enhanced anti-tumor response. Interestingly, targeting BCL9/BCL9L enhances the antigen presentation ability of cDC1 and promotes the infiltration of cDC1 and CD8+T cells into tumors, highlighting the key role of this approach in enhancing cDC1-mediated anti-tumor immunity. The therapy aimed at improving antigen presentation may benefit from the combined use of BCL9 inhibitors.
Related Products and Services
CD Antigens Targets of CAR-T Cell Therapy Cytokines Cancer Drug Targets Immune Checkpoint Proteins Protein Interaction Service Protein Expression and Purification Services Drug Discovery Screening Protein Pathway Profiling
Reference He F, Wu Z, Liu C, Zhu Y, Zhou Y, Tian E, Rosin-Arbesfeld R, Yang D, Wang MW, Zhu D. Targeting BCL9/BCL9L enhances antigen presentation by promoting conventional type 1 dendritic cell (cDC1) activation and tumor infiltration. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 May 29;9(1):139. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01838-9. PMID: 38811552; PMCID: PMC11137111.
