Thu, 2016/07/21
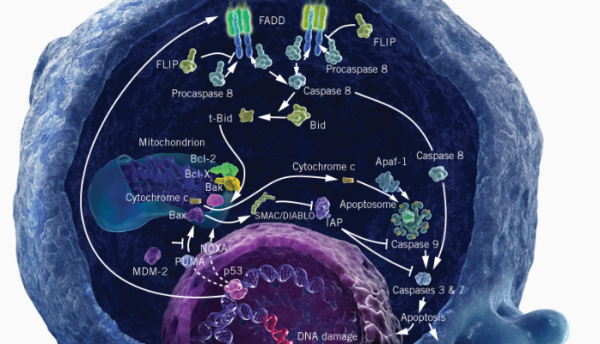
Cyclin in Tumor: Cdk5 Disruption Promotes Antitumor Immunity
Thu, 2016/07/14
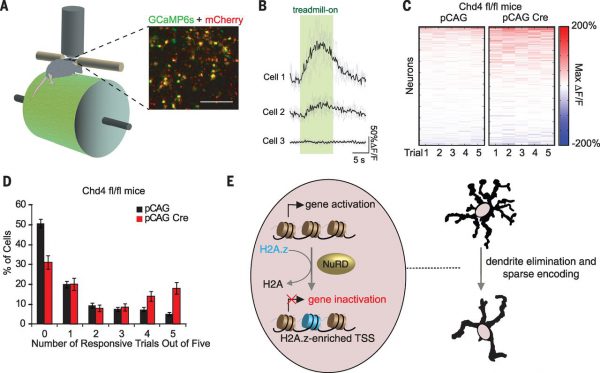
Neural Epigenetic Regulation: Chromatin Remodeling Regulates Genes and Neural Coding

Fri, 2016/07/01
Autoimmune Diseases Therapy: Targeted by Chimeric Antigen Receptor T cells
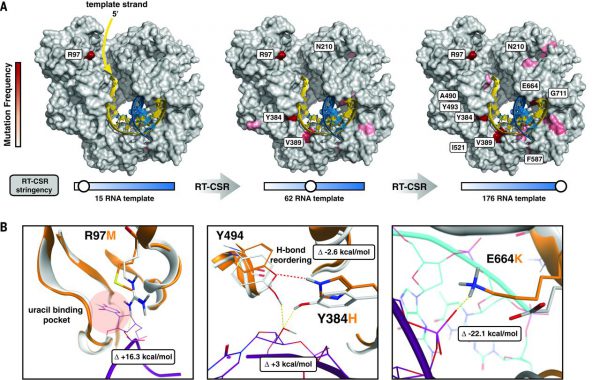
Thu, 2016/06/23
Tue, 2016/06/21
Therapeutic Targets for Skin Cancer: MET Signaling and RAS Converge on EGFR

Fri, 2016/06/17
New Fluorescent Method to Detect Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+)
Thu, 2016/06/16
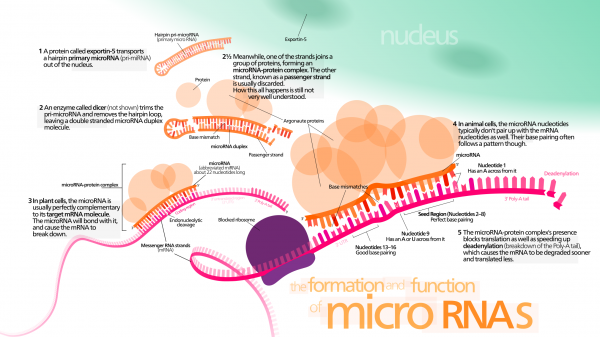
Perspective: Using microRNAs to Induce Single-cell variability
Thu, 2016/05/26
Insight: the Mechanism to Maintain the Spindle at the Cell Center during Mitosis
