Uncategorized Sunday, 2024/02/18
Breastfeeding can provide significant health benefits for newborns and infants by providing nutrition, immune protection, and shaping the gut microbiota. Although scientists have long believed that breast milk contains complement components, the physiological correlation of complement components in breast milk is not clear to them. Recently, a research report titled "Complement in breast milk modifies offspring gut microbiota to promote infant health " was published in the journal Cell. Scientists from institutions such as Johns Hopkins University found through their research that immune components called the complement system in breast milk may shape the intestinal environment of young mice and make them less susceptible to bacteria that cause specific diseases.
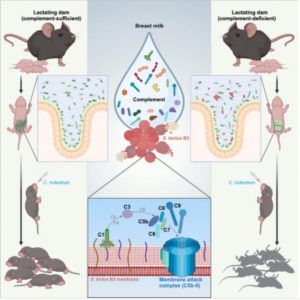
Researchers have found that compared to mouse offspring breastfed with standard mice, mouse offspring fed without key complement proteins in breast milk often have different gut microbiota, which may make them more susceptible to Citrobacter rodentium, a bacterium that can infect the intestines of mice, similar to Escherichia coli that infects human (not mouse) bodies. Researchers have shown that complement components in mouse breast milk can enhance the physical health of mouse offspring by directly eliminating certain types of gut microbiota. The reshaping of this gut microbiota makes young mice less susceptible to infection with Mycobacterium citrate, thereby protecting them from certain infectious threats. This reshaping activity often does not rely on antibodies, contrary to the way complement components are typically believed to function.
Our Featured Products
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Source | Species | Tag |
| C3-10522H | Recombinant Human C3, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His |
| Complement C3d-48H | Native Human Complement C3d | Human Plasma | Human | N/A |
| C3b-08H | Native Human Complement C3 beta protein | Human Serum | Human | N/A |
| C3-10H | Active Recombinant Human C3 protein, His-tagged | HEK293 | Human | His |
| C3-603H | Active Recombinant Human C3 | E.coli | Human | N/A |
| C3-01H | Active Recombinant Human C3 Protein | E.coli | Human | N/A |
| C5-4756H | Active Recombinant Human C5 protein | E.coli | Human | N/A |
| C5-10539H | Recombinant Human C5, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His |
| C5-10540H | Active Native Human C5 | Human Serum | Human | N/A |
| C2-6878H | Active Recombinant Human C2 protein(Met1-Leu752), His-tagged | HEK293 | Human | C-His |
Researchers have also confirmed in separate in vitro analyses that human breast milk contains these complement components, which can exhibit similar activity in targeting specific bacteria. Relevant research findings may reveal the molecular mechanisms behind how breast milk functions to protect against specific bacterial infections. Researcher Fengyi Wan said that these findings reveal the crucial role that complement proteins in breast milk play in shaping the gut microbiota composition of offspring and protecting the gut from bacterial infections in the early stages. This also represents an important extension for scientists in understanding the protective mechanism of breast milk. Breastfeeding has many known and suspected benefits, as it can provide better nutrition for infants and seems to help the body resist some short-term or long-term diseases. Breast milk can also help prevent common infections by sharing antibodies and white blood cells from the mother's body; In addition, breast milk also contains some complement proteins that can work together with complement antibodies to attack bacteria. Although complement proteins circulating in the blood have always been the focus of many studies, there is much less research on complement proteins in breast milk, and researchers are still unclear about their effects until now.
In summary, the research results of this article indicate that by selectively clearing symbiotic gut microbiota, different components from breast milk can shape the gut microbiota composition of newborns and infants, thereby protecting the body from infection by environmental pathogens such as Lactobacillus.
Related Products and Services
Immune Checkpoint Proteins Protein Interaction Service Protein Expression and Purification Services Biomarker Service Drug Discovery Screening Protein Pathway Profiling Protein Expression Microarray
Reference Dongqing Xu, Siyu Zhou, Yue Liu, et al. Complement in breast milk modifies offspring gut microbiota to promote infant health, Cell (2024). DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2023.12.019
