Uncategorized Tuesday, 2017/09/05
ABP215 is a biosimilar drug developed by Amgen and Allergan, using Avastin (bevacizumab) as a prototype drug. Amgen filed a drug application to the FDA in November 2016. The FDA Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee (ODAC) met on July 13, 2017, and the members voted in favor of approving the ABP215 drug application. The ABP215 is expected to become America's first Avastin bio-similar drug.
Liu Shining, the research manager in TrendForce, pointed out that, in the process of FDA review biosimilar, we can see it’s quite different from the review of new drug. Biosimilar focuses more on the similarities among physical and chemical characteristics, biological functional characteristics, and pharmacokinetics/efficacy, then comes to preclinical and clinical trial data. This is quite different with the innovative drug review which pay more attention on the data in clinical phase II to clinical phase III.
In order to confirm the similarity between ABP215 and Avastin, it can be seen from Figure 1 that the two drugs compare ranges of items, and each item involves more than one subdivision analysis items. For example, the primary structure item uses 17 analytical subdivision to confirm the similarity of the amino acid sequence homogeneity and the glycosylation performance. In addition, from the secondary to quaternary structure, VEGFA binding affinity and many other biological function characteristics, also show similarity between the two drugs through a variety of analysis. Overall, although there are some qualitative difference between the two drugs, the subsequent clinical trial data do not show that these differences could lead to differences in clinical efficacy and safety.
Fig1. Comparison of structural and biological function between ABP215 and Avastin
In the clinical trial section, Amgen performed two clinical trials, Study 20110216 (Trial 216) and Study20120265 (referred to as Test 265), as shown in Table 1. The objective of Trial 216 is to observe the pharmacokinetics, safety, immunogenicity of ABP215 and Avastin. Test 265 targets non-small cell lung cancer patients and adds an evaluation assay of efficacy performance.Table 1. ABP215 Clinical Trial
| Test name | Object | Test type | Test design | Number of subjects | Time | clinical trial endpoint |
| Study20110216 | Healthy male | Pharmacokinetics, safety, Immunogenicity | Randomly assigned, single-blind, three-arm, parallel-group | 202 | 85 days | Cmax, AUClet |
| Study20120265NCT01966003 | Non-small cell lung cancer | Efficacy, safety, Immunogenicity | Randomly assigned, double-blind, two-arm, parallel-group | 642(ITT) | 18 weeks | ORR |
The results of the trial 216 show that the pharmacokinetic performance of ABP215, United States approved Avastin and the EU approved bevacizumab, as shown in Figure 2, are all in the 90% confidence interval. The difference between the area average of concentration in blood on the time under the curve of (AUC0-∞, AUC0-t) and the average of maximum concentrations in the blood (CMax) ranged from 80% to 125%, which concluded the similarity of pharmacokinetic performance between the biosimilar and prototype.
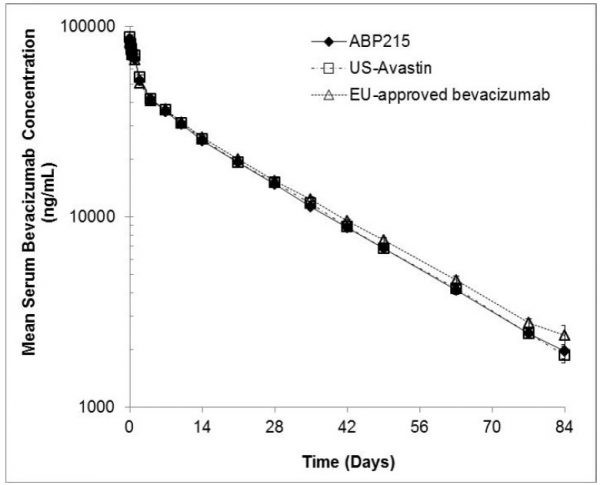 Fig 2. Pharmacokinetics of ABP and Avastin
Fig 2. Pharmacokinetics of ABP and Avastin
Table 2 Comparison of ABP215 with EU approved Avastin in clinical efficacy
| Clinical indicators | ABP215 (n=328) N (%) | EU-Avastin (n=314) N (%) |
| ORR | 128 (39.0) | 131 (41.7) |
| Risk ratio (90% CI) | 0.93 (0.8-1.09) | |
| CR | 2 (0.6) | 2 (0.6) |
| PR | 126 (38.4) | 129 (41.1) |
| SD | 144 (43.9) | 137 (43.6) |
| PD | 21 (6.4) | 18 (5.7) |
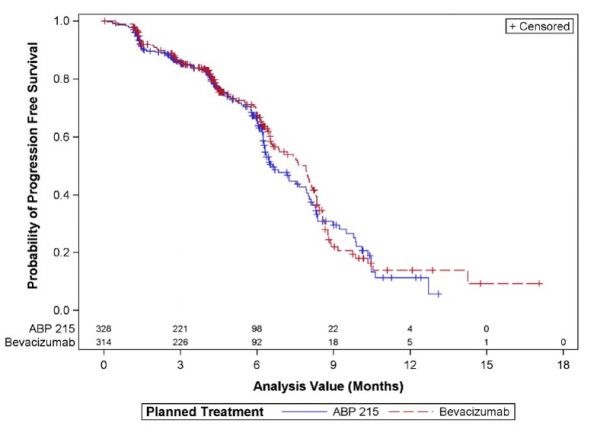 Fig3. Comparison of ABP215 with EU approval of Avastin at PFS
Fig3. Comparison of ABP215 with EU approval of Avastin at PFS
